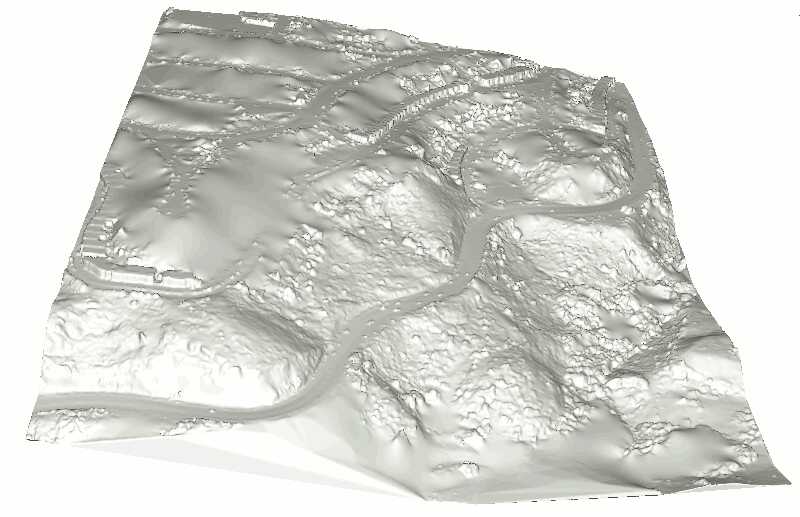
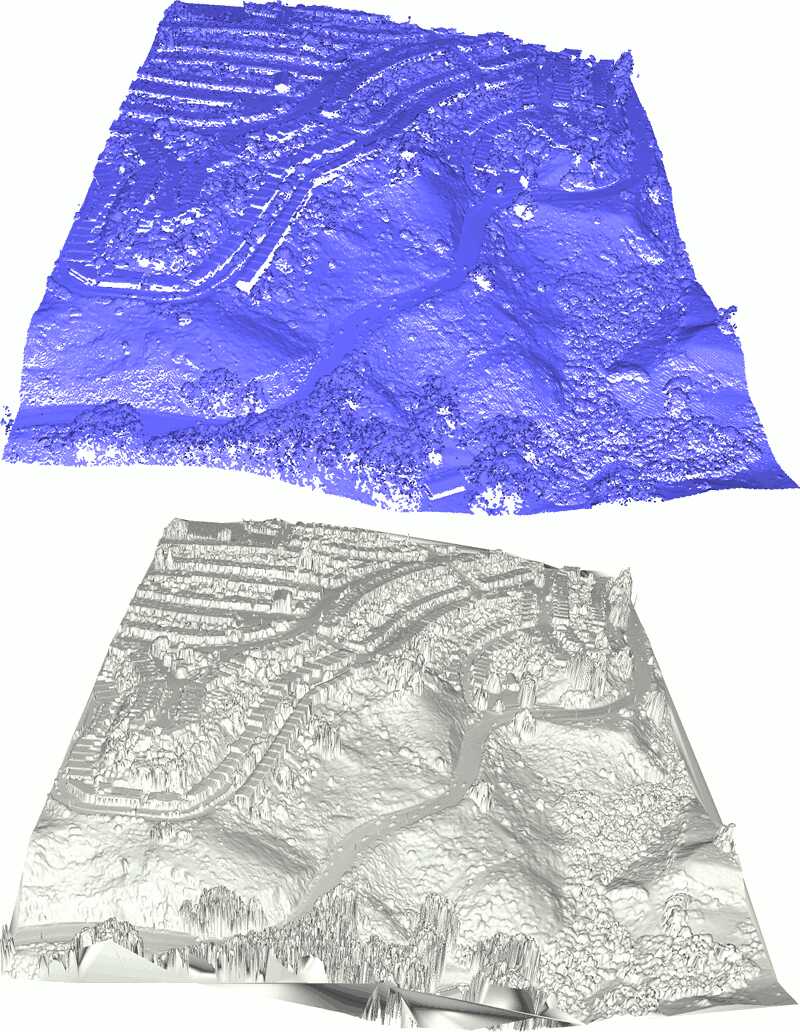
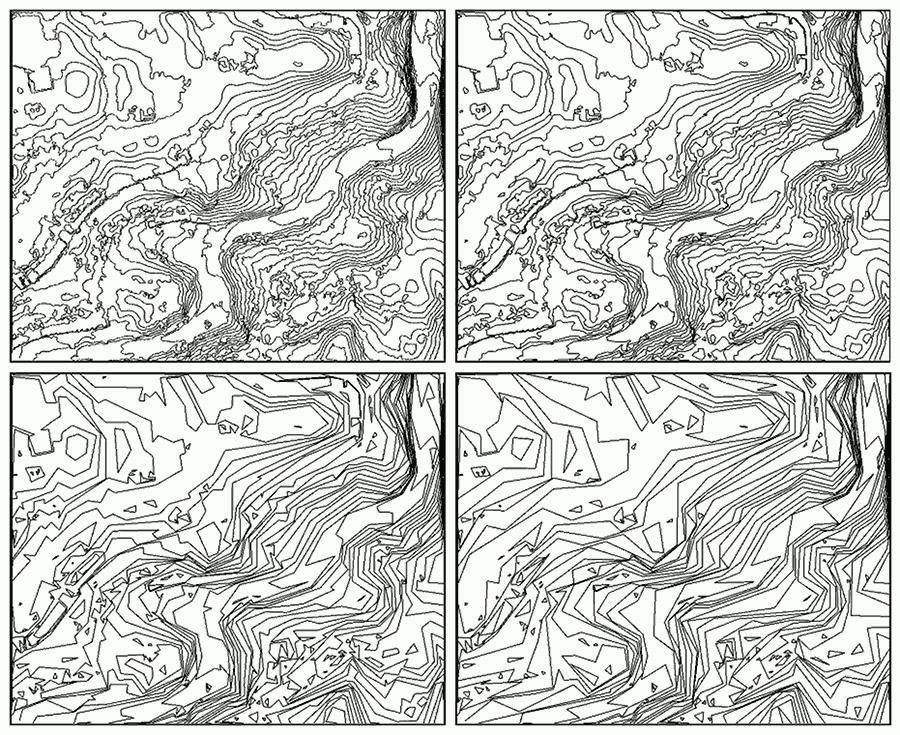
在GIS应用中常用的传感器(如激光雷达LIDAR)会生成密集的点云数据。这类应用通常需要使用更高级的数据结构,例如不规则三角网(Triangulated Irregular Network, TIN),它可以作为数字高程模型(Digital Elevation Model, DEM)的基础,特别是用于生成数字地形模型(Digital Terrain Model, DTM)。点云数据还可以通过分类信息进行扩充,将点分为地面、植被和建筑物等用户自定义的类别。
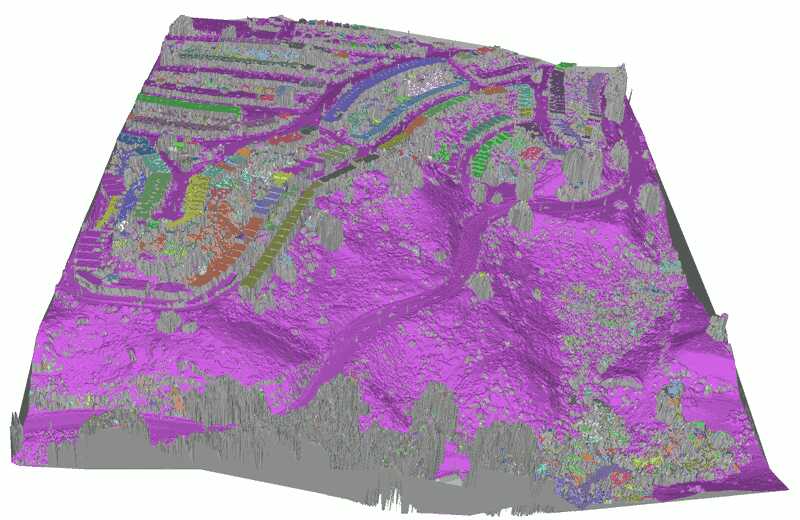
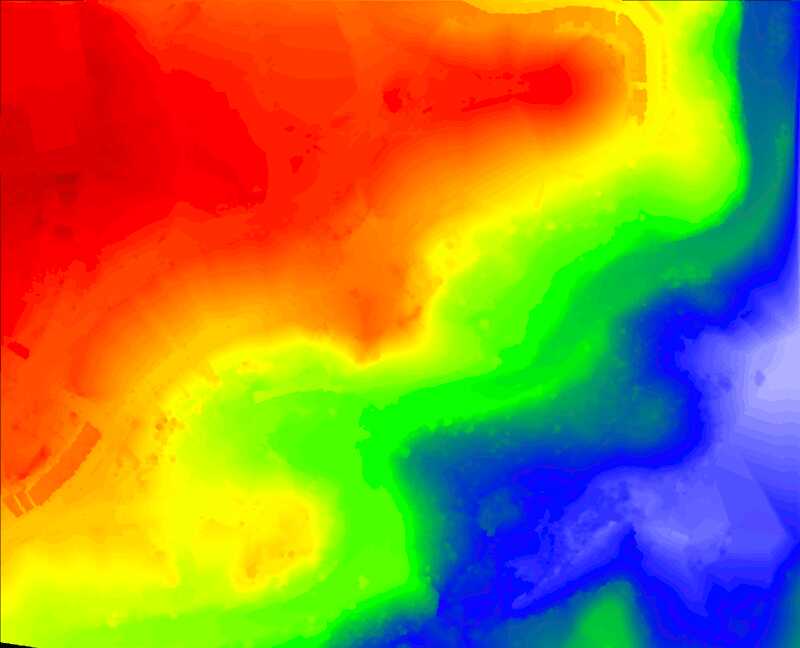
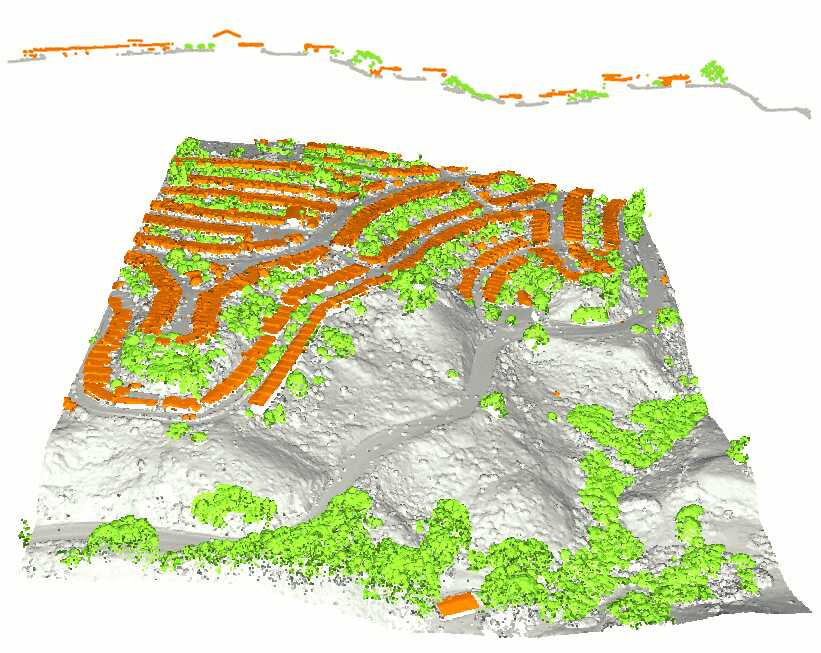
本教程将演示以下处理流程:首先从输入的点云数据计算出以TIN形式存储的DSM。然后,过滤掉对应于建筑物立面或植被噪声的过大面片。保留对应于地面的大型连通分量。填充空洞并对获得的DEM进行重新网格化。从中生成栅格DEM和等高线。最后,执行有监督的三类别分类,将点分为植被、建筑物和地面。
CGAL提供了多种三角剖分数据结构和算法。TIN可以通过结合二维Delaunay三角剖分和投影特征来生成:使用点在选定平面(通常是XY平面)上的二维位置计算三角剖分结构,同时保留点的三维位置用于可视化和测量。
得益于CGAL Delaunay三角剖分灵活的API,我们的TIN可以在顶点和/或面上添加信息。在本例中,每个顶点记录输入点云中对应点的索引(这将用于后续过滤地面点),每个面则被赋予其连通分量的索引。
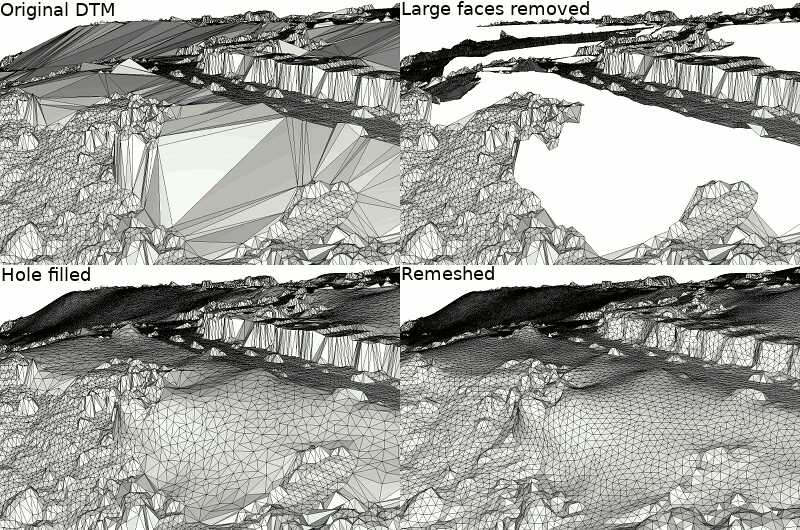
由于简单地移除建筑物覆盖的大面积区域内的顶点会导致Delaunay面片过大,无法很好地表示DTM的3D特征,因此可以通过额外的步骤来生成更好的网格形状:移除大于阈值的面片,然后使用空洞填充算法对空洞进行三角剖分、细化和平滑处理。
由于最后两个步骤(空洞填充和重网格化)是在3D网格上执行的,我们的DTM作为2.5D表示的假设可能不再有效。因此,我们首先使用最后计算的各向同性DTM网格的顶点重建TIN。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Projection_traits_xy_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Delaunay_triangulation_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Triangulation_vertex_base_with_info_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Triangulation_face_base_with_info_2.h>
#include <CGAL/boost/graph/graph_traits_Delaunay_triangulation_2.h>
#include <CGAL/boost/graph/copy_face_graph.h>
#include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h>
#include <CGAL/compute_average_spacing.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/locate.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/triangulate_hole.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/border.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/remesh.h>
#include <boost/graph/adjacency_list.hpp>
#include <CGAL/boost/graph/split_graph_into_polylines.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/WKT.h>
#include <CGAL/Constrained_Delaunay_triangulation_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Constrained_triangulation_plus_2.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyline_simplification_2/simplify.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyline_simplification_2/Squared_distance_cost.h>
#include <CGAL/Classification.h>
#include <CGAL/Random.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <queue>
#include "include/Color_ramp.h"
using Vbi = CGAL::Triangulation_vertex_base_with_info_2 <Point_set::Index, Projection_traits>;
#ifdef CGAL_LINKED_WITH_TBB
#else
#endif
bool face_has_isovalue (TIN::Face_handle fh, double isovalue)
{
bool above = false, below = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++ i)
{
if (fh->vertex(i)->point().z() > isovalue)
above = true;
if (fh->vertex(i)->point().z() < isovalue)
below = true;
}
return (above && below);
}
Segment_3 isocontour_in_face (TIN::Face_handle fh,
double isovalue)
{
bool source_found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++ i)
{
Point_3 p0 = fh->vertex((i+1) % 3)->point();
Point_3 p1 = fh->vertex((i+2) % 3)->point();
if ((p0.z() - isovalue) * (p1.z() - isovalue) > 0)
continue;
double zbottom = p0.z();
double ztop = p1.z();
if (zbottom > ztop)
{
std::swap (zbottom, ztop);
std::swap (p0, p1);
}
double ratio = (isovalue - zbottom) / (ztop - zbottom);
if (source_found)
target = p;
else
{
source = p;
source_found = true;
}
}
}
template <typename Graph>
class Polylines_visitor
{
private:
std::vector<std::vector<Point_3> >& polylines;
Graph& graph;
public:
Polylines_visitor (Graph& graph, std::vector<std::vector<Point_3> >& polylines)
: polylines (polylines), graph(graph) { }
void start_new_polyline()
{
polylines.push_back (std::vector<Point_3>());
}
void add_node (typename Graph::vertex_descriptor vd)
{
polylines.back().push_back (graph[vd]);
}
void end_polyline()
{
if (polylines.back().size() < 50)
polylines.pop_back();
}
};
using CDT_vertex_base = PS::Vertex_base_2<Projection_traits>;
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
const std::string fname = argc != 2 ? CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/b9_training.ply") : argv[1];
if (argc != 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " points.ply" << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Running with default value " << fname << "\n";
}
std::ifstream ifile (fname, std::ios_base::binary);
ifile >> points;
std::cerr << points.size() << " point(s) read" << std::endl;
Mesh dsm_mesh;
std::ofstream dsm_ofile ("dsm.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
dsm_ofile.close();
auto idx_to_point_with_info
= [&](const Point_set::Index& idx) -> std::pair<Point_3, Point_set::Index>
{
return std::make_pair (points.
point(idx), idx);
};
TIN_with_info tin_with_info
(boost::make_transform_iterator (points.
begin(), idx_to_point_with_info),
boost::make_transform_iterator (points.
end(), idx_to_point_with_info));
double spacing = CGAL::compute_average_spacing<Concurrency_tag>(points, 6);
spacing *= 2;
auto face_height
= [&](const TIN_with_info::Face_handle fh) -> double
{
double out = 0.;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++ i)
out = (std::max) (out,
CGAL::abs(fh->vertex(i)->point().z() - fh->vertex((i+1)%3)->point().z()));
return out;
};
for (TIN_with_info::Face_handle fh : tin_with_info.all_face_handles())
if (tin_with_info.is_infinite(fh) || face_height(fh) > spacing)
fh->info() = -2;
else
fh->info() = -1;
std::vector<int> component_size;
for (TIN_with_info::Face_handle fh : tin_with_info.finite_face_handles())
{
if (fh->info() != -1)
continue;
std::queue<TIN_with_info::Face_handle> todo;
todo.push(fh);
int size = 0;
while (!todo.empty())
{
TIN_with_info::Face_handle current = todo.front();
todo.pop();
if (current->info() != -1)
continue;
current->info() = int(component_size.size());
++ size;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++ i)
todo.push (current->neighbor(i));
}
component_size.push_back (size);
}
std::cerr << component_size.size() << " connected component(s) found" << std::endl;
Mesh tin_colored_mesh;
Mesh::Property_map<Mesh::Face_index, CGAL::IO::Color>
color_map = tin_colored_mesh.add_property_map<Mesh::Face_index,
CGAL::IO::Color>(
"f:color").first;
CGAL::parameters::face_to_face_output_iterator
(boost::make_function_output_iterator
([&](const std::pair<TIN_with_info::Face_handle, Mesh::Face_index>& ff)
{
if (ff.first->info() < 0)
else
{
CGAL::Random r (ff.first->info());
color_map[ff.second] = CGAL::IO::Color (r.get_int(64, 192),
r.get_int(64, 192),
r.get_int(64, 192));
}
})));
std::ofstream tin_colored_ofile ("colored_tin.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
tin_colored_ofile.close();
int min_size = int(points.size() / 2);
std::vector<TIN_with_info::Vertex_handle> to_remove;
for (TIN_with_info::Vertex_handle vh : tin_with_info.finite_vertex_handles())
{
TIN_with_info::Face_circulator circ = tin_with_info.incident_faces (vh),
start = circ;
bool keep = false;
do
{
if (circ->info() >= 0 && component_size[std::size_t(circ->info())] > min_size)
{
keep = true;
break;
}
}
while (++ circ != start);
if (!keep)
to_remove.push_back (vh);
}
std::cerr << to_remove.size() << " vertices(s) will be removed after filtering" << std::endl;
for (TIN_with_info::Vertex_handle vh : to_remove)
tin_with_info.remove (vh);
Mesh dtm_mesh;
std::vector<Mesh::Face_index> face_selection;
Mesh::Property_map<Mesh::Face_index, bool> face_selection_map
= dtm_mesh.add_property_map<Mesh::Face_index, bool>("is_selected", false).first;
CGAL::parameters::face_to_face_output_iterator
(boost::make_function_output_iterator
([&](const std::pair<TIN_with_info::Face_handle, Mesh::Face_index>& ff)
{
double longest_edge = 0.;
bool border = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++ i)
{
(ff.first->vertex((i+1)%3)->point(),
ff.first->vertex((i+2)%3)->point()));
TIN_with_info::Face_circulator circ
= tin_with_info.incident_faces (ff.first->vertex(i)),
start = circ;
do
{
if (tin_with_info.is_infinite (circ))
{
border = true;
break;
}
}
while (++ circ != start);
if (border)
break;
}
if (!border && longest_edge > limit)
{
face_selection_map[ff.second] = true;
face_selection.push_back (ff.second);
}
})));
std::ofstream dtm_ofile ("dtm.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
dtm_ofile.close();
std::cerr << face_selection.size() << " face(s) are selected for removal" << std::endl;
face_selection.clear();
for (Mesh::Face_index fi : faces(dtm_mesh))
if (face_selection_map[fi])
face_selection.push_back(fi);
std::cerr << face_selection.size() << " face(s) are selected for removal after expansion" << std::endl;
for (Mesh::Face_index fi : face_selection)
dtm_mesh.collect_garbage();
if (!dtm_mesh.is_valid())
std::cerr << "Invalid mesh!" << std::endl;
std::ofstream dtm_holes_ofile ("dtm_with_holes.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
dtm_holes_ofile.close();
std::vector<Mesh::Halfedge_index> holes;
std::cerr << holes.size() << " hole(s) identified" << std::endl;
double max_size = 0.;
Mesh::Halfedge_index outer_hull;
for (Mesh::Halfedge_index hi : holes)
{
{
const Point_3& p = dtm_mesh.point(target(haf, dtm_mesh));
hole_bbox += p.bbox();
}
if (size > max_size)
{
max_size = size;
outer_hull = hi;
}
}
for (Mesh::Halfedge_index hi : holes)
if (hi != outer_hull)
(dtm_mesh, hi, CGAL::parameters::fairing_continuity(0));
std::ofstream dtm_filled_ofile ("dtm_filled.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
dtm_filled_ofile.close();
std::ofstream dtm_remeshed_ofile ("dtm_remeshed.ply", std::ios_base::binary);
dtm_remeshed_ofile.close();
TIN dtm_clean (dtm_mesh.points().begin(), dtm_mesh.points().end());
std::size_t width = 1920;
std::cerr << "Rastering with resolution " << width << "x" << height << std::endl;
std::ofstream raster_ofile ("raster.ppm", std::ios_base::binary);
raster_ofile << "P6" << std::endl
<< width << " " << height << std::endl
<< 255 << std::endl;
Color_ramp color_ramp;
TIN::Face_handle location;
for (std::size_t y = 0; y < height; ++ y)
for (std::size_t x = 0; x < width; ++ x)
{
0);
location = dtm_clean.locate (query, location);
std::array<unsigned char, 3> colors { 0, 0, 0 };
if (!dtm_clean.is_infinite(location))
{
(
Point_2 (location->vertex(0)->point().x(), location->vertex(0)->point().y()),
Point_2 (location->vertex(1)->point().x(), location->vertex(1)->point().y()),
Point_2 (location->vertex(2)->point().x(), location->vertex(2)->point().y()),
double height_at_query
colors = color_ramp.get(height_ratio);
}
raster_ofile.write (reinterpret_cast<char*>(&colors), 3);
}
raster_ofile.close();
double gaussian_variance = 4 * spacing * spacing;
for (TIN::Vertex_handle vh : dtm_clean.finite_vertex_handles())
{
double z = vh->point().z();
double total_weight = 1;
TIN::Vertex_circulator circ = dtm_clean.incident_vertices (vh),
start = circ;
do
{
if (!dtm_clean.is_infinite(circ))
{
double weight = std::exp(- sq_dist / gaussian_variance);
z += weight * circ->point().z();
total_weight += weight;
}
}
while (++ circ != start);
z /= total_weight;
vh->point() =
Point_3 (vh->point().x(), vh->point().y(), z);
}
std::array<double, 50> isovalues;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < isovalues.size(); ++ i)
using Segment_graph = boost::adjacency_list<boost::listS, boost::vecS, boost::undirectedS, Point_3>;
Segment_graph graph;
using Map_p2v = std::map<Point_3, Segment_graph::vertex_descriptor>;
Map_p2v map_p2v;
for (TIN::Face_handle vh : dtm_clean.finite_face_handles())
for (double iv : isovalues)
if (face_has_isovalue (vh, iv))
{
Segment_3 segment = isocontour_in_face (vh, iv);
for (
const Point_3& p : { segment.source(), segment.target() })
{
Map_p2v::iterator iter;
bool inserted;
std::tie (iter, inserted) = map_p2v.insert (std::make_pair (p, Segment_graph::vertex_descriptor()));
if (inserted)
{
iter->second = boost::add_vertex (graph);
graph[iter->second] = p;
}
}
boost::add_edge (map_p2v[segment.source()], map_p2v[segment.target()], graph);
}
std::vector<std::vector<Point_3> > polylines;
Polylines_visitor<Segment_graph> visitor (graph, polylines);
std::cerr << polylines.size() << " polylines computed, with "
<< map_p2v.size() << " vertices in total" << std::endl;
std::ofstream contour_ofile ("contour.wkt");
contour_ofile.precision(18);
contour_ofile.close();
CTP ctp;
for (const std::vector<Point_3>& poly : polylines)
ctp.insert_constraint (poly.begin(), poly.end());
PS::simplify (ctp, PS::Squared_distance_cost(), PS::Stop_above_cost_threshold (16 * spacing * spacing));
polylines.clear();
for (CTP::Constraint_id cid : ctp.constraints())
{
polylines.push_back (std::vector<Point_3>());
polylines.back().reserve (ctp.vertices_in_constraint (cid).size());
for (CTP::Vertex_handle vh : ctp.vertices_in_constraint(cid))
polylines.back().push_back (vh->point());
}
std::size_t nb_vertices
= std::accumulate (polylines.begin(), polylines.end(), std::size_t(0),
[](std::size_t size, const std::vector<Point_3>& poly) -> std::size_t
{ return size + poly.size(); });
std::cerr << nb_vertices
<< " vertices remaining after simplification ("
<< 100. * (nb_vertices / double(map_p2v.size())) << "%)" << std::endl;
std::ofstream simplified_ofile ("simplified.wkt");
simplified_ofile.precision(18);
simplified_ofile.close();
std::optional<Point_set::Property_map<int>> training_map = points.
property_map<
int>(
"training");
if (training_map.has_value())
{
std::cerr << "Classifying ground/vegetation/building" << std::endl;
Classification::Label_set labels ({ "ground", "vegetation", "building" });
Classification::Point_set_feature_generator<Kernel, Point_set, Point_set::Point_map>
#ifdef CGAL_LINKED_WITH_TBB
generator.generate_point_based_features (features);
#else
generator.generate_point_based_features (features);
#endif
Classification::ETHZ::Random_forest_classifier classifier (labels, features);
classifier.train (points.
range(training_map.value()));
Point_set::Property_map<int> label_map = points.
add_property_map<
int>(
"labels").first;
Classification::classify_with_graphcut<Concurrency_tag>
(points, points.
point_map(), labels, classifier,
generator.neighborhood().k_neighbor_query(12),
0.5f,
12,
label_map);
std::cerr << "Mean IoU on training data = "
<< Classification::Evaluation(labels,
points.
range(training_map.value()),
points.
range(label_map)).mean_intersection_over_union() << std::endl;
std::ofstream classified_ofile ("classification_gis_tutorial.ply");
classified_ofile << points;
classified_ofile.close();
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
unspecified_type features()
CGAL::Bbox_3 bbox(const PolygonMesh &pmesh, const NamedParameters &np=parameters::default_values())